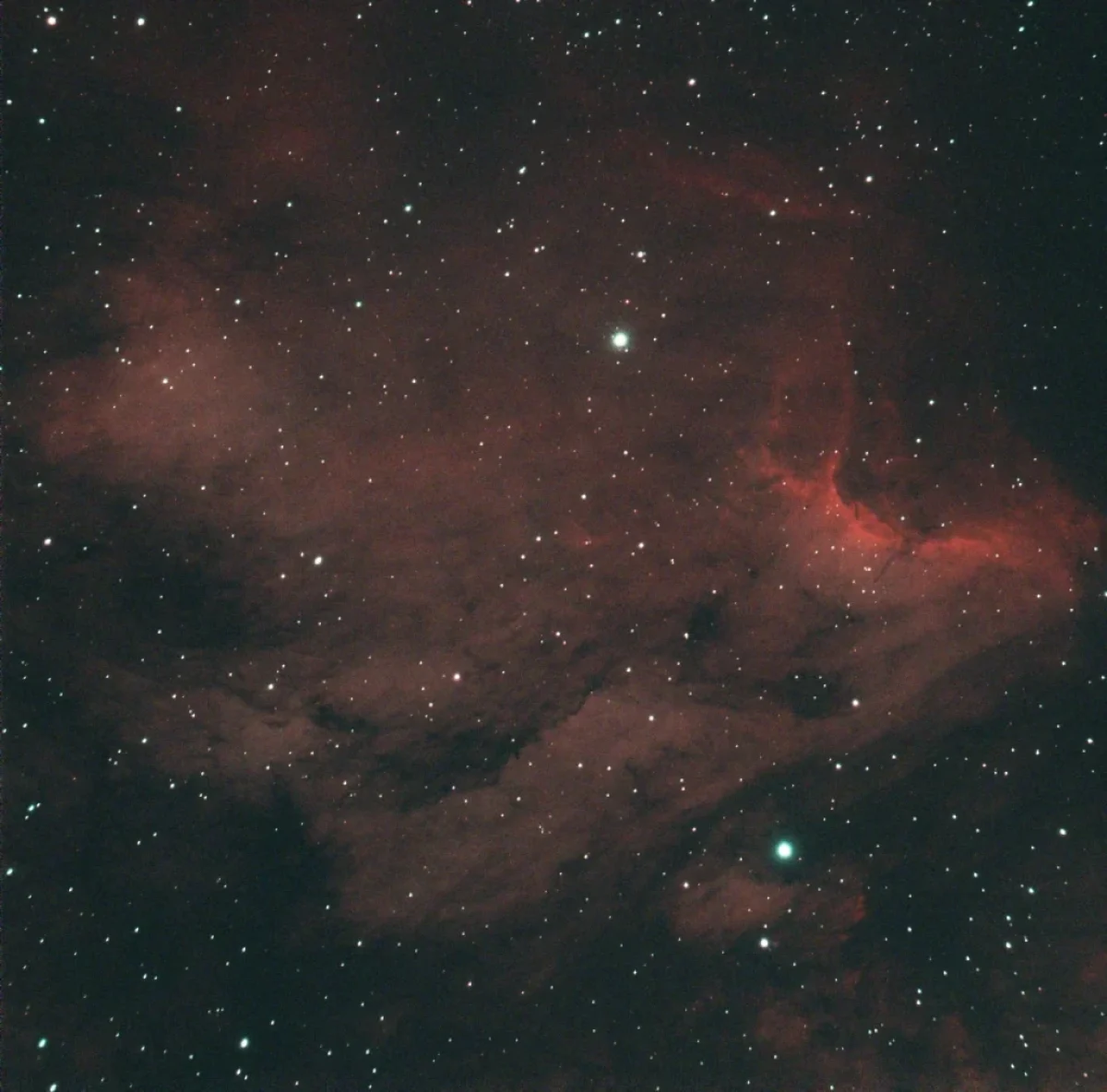
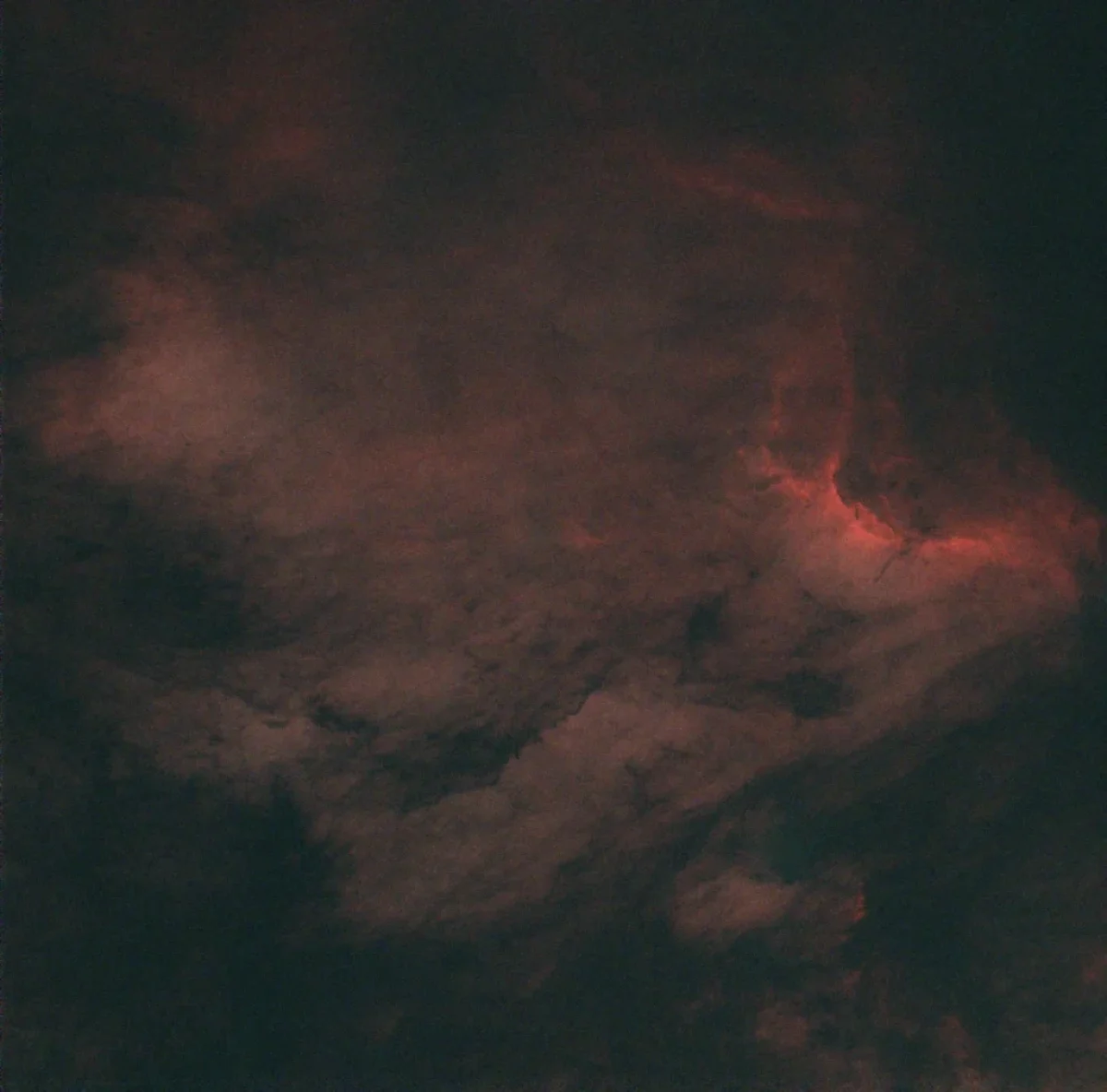
The North America Nebula with (and without) stars
July 9th, 2022: great imaging session with the North America Nebula and the Pelican Nebula in Cygnus. With the ZWO EAF firmware upgrade I was also able to dramatically improve the autofocus routine.
In the next paragraphs I would like to guide you through my setup and the image acquisition process for these targets.
- I started my session at 9:30pm EDT by setting up the telescope, the mount, cables, guiding scope, imaging camera and filters. I found a sweet spot on my driveway, where the sky is free from obstacles to the North, East and South. There is light pollution because of the street lamps, but my objective was to capture my targets with a narrowband filter (the Optolong l-Extreme), which has narrow 7nm band passes in the Hydrogen alpha (Ha) and Oxygen III (OIII) lines only, and blocks the light pollution.
- Second, I balanced the mount and the telescope and turned on my laptop and launched Remote Desktop, to control my mini PC, where the acquisition software (NINA) is running.
- I roughly polar aligned my telescope, turned on my mount and performed a quick align procedure (no need to perform a 2 star alignment, as I polar aligned the mount and “plate solved” my imaging targets later on).
- I connected all my equipment: camera, manual filter wheel, focuser, mount, guider. I also told NINA to cool my imaging camera to -10°C.
- Next, I launched the autofocus routine (and after the firmware upgrade it worked like a charm!)
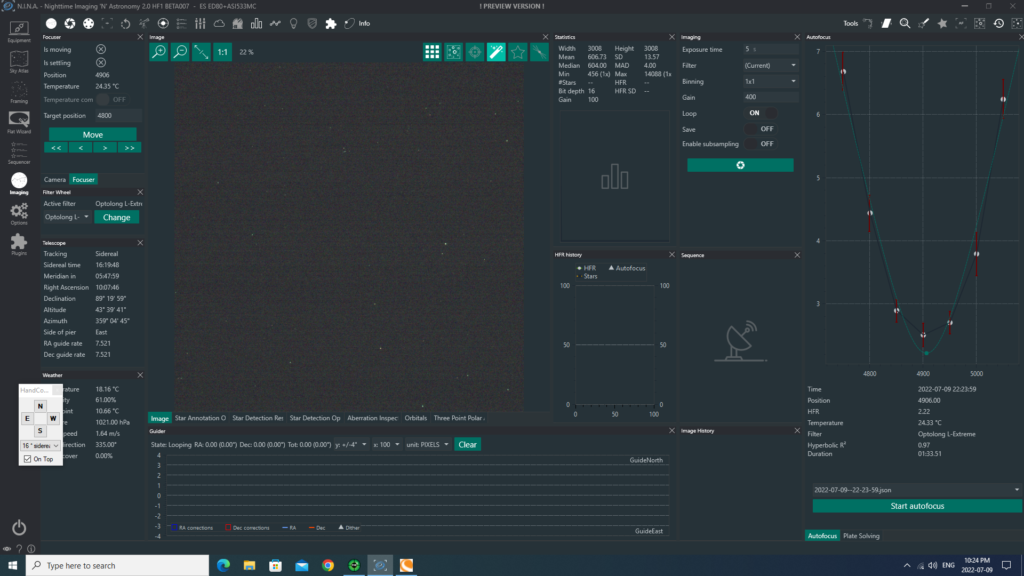
After the ZWO EAF electronic focuser firmware update, NINA Autofocus routine returned an almost perfect hyperbole (as you can see on the right side of this image) - I polar aligned my mount with the “Three Point Polar Alignment” NINA plugin (and the help of my neighbour, who was reading the error values while I was ), which led me to an accuracy consistently under 1 arcsecond during the guiding with PHD2.
- Next, I slewed the scope to my first target: the Cygnus Wall (part of the North America Nebula, NGC7000).
- I told PHD2 to perform a mount calibration and to start guiding
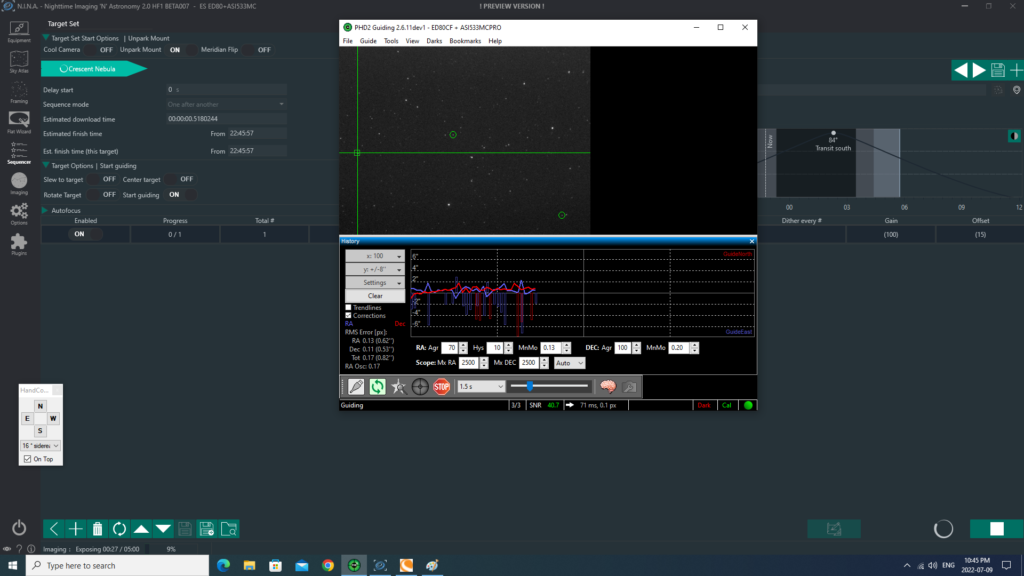
Guiding looks good (with a total RMS error of 0.82″) - Next step, I launched an imaging sequence with NINA: 30×180 seconds exposures (with dithering every 3 images).
- At the end of the session, I took 20 flat frames (they are essentials to remove uneven illumination and dust spots from the images).
- Finally, I stacked and processed the images with PixInsight (below you can see the result of my effort)
When the first image appeared on the screen of my laptop I had a aha moment and immediately realized that the imaging session would have been above my expectations.
Setup
Scope: Explore Scientific ED80CF APO refractor
Mount: Celestron AVX mount
Imaging Camera: ZWO ASI533 MC PRO (cooled at -10°C)
Filters: Optolong L-Extreme
Guiding camera: ZWO ASI224 MC with a IR Cut filter, PHD2
Guide Scope: Orion Deluxe Mini 50mm Guide Scope.
Software: NINA, PixInsight
Total Integration Time: 1 hour (20x180s, dark, flat, bias)
The North America Nebula (NGC 7000) in Cygnus constellation is a bright emission nebula, close to Deneb (the brightest star in Cygnus).
For the first time, while processing and stacking the images I used the Starnet v2 module for PixInsight and I created a “starless” image. I think that Starnet is a cool add-on which can increase the details of nebulae.
Note: Scroll the slider to switch between the images of the North America Nebula with the stars and its starless version.
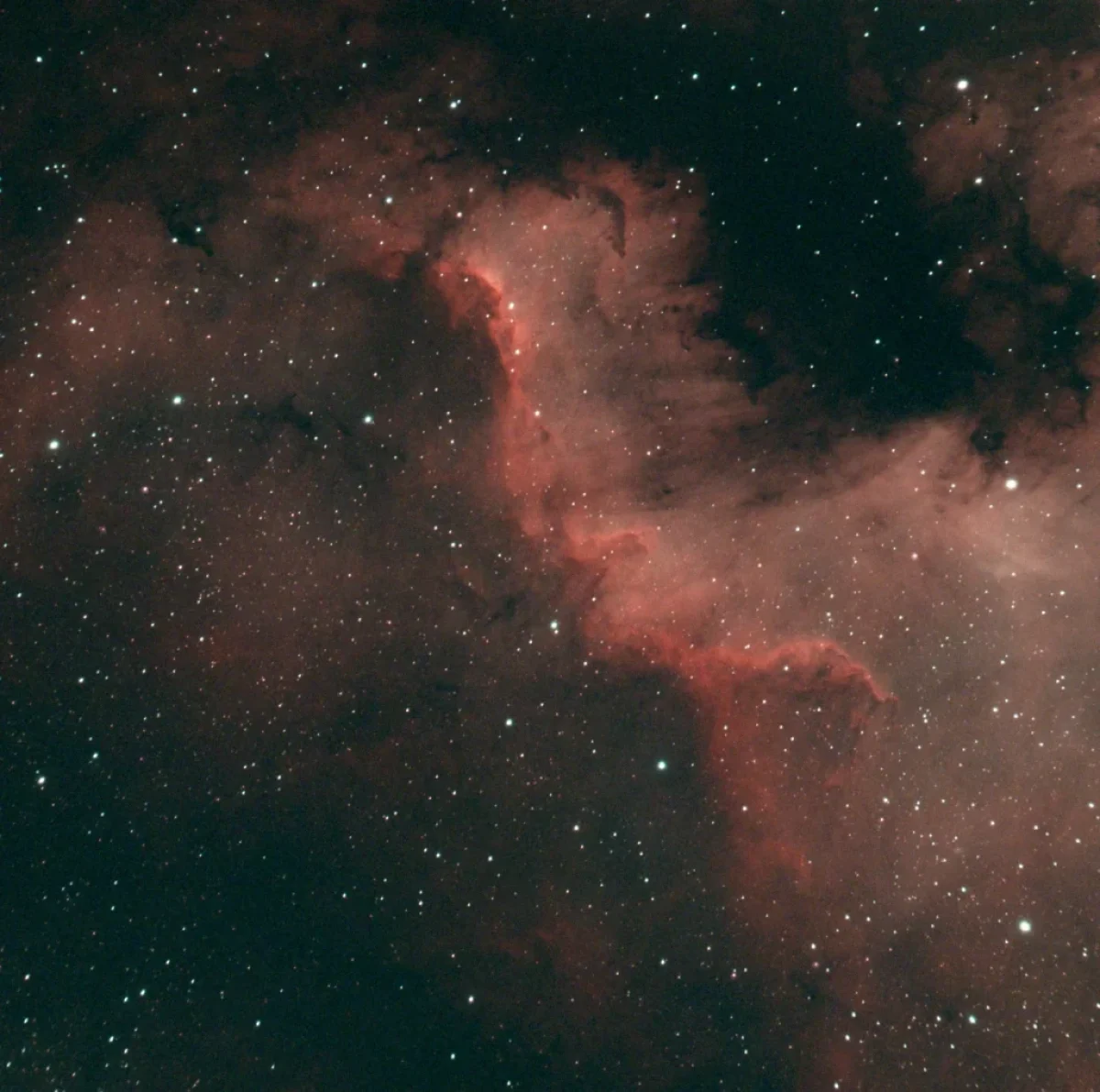
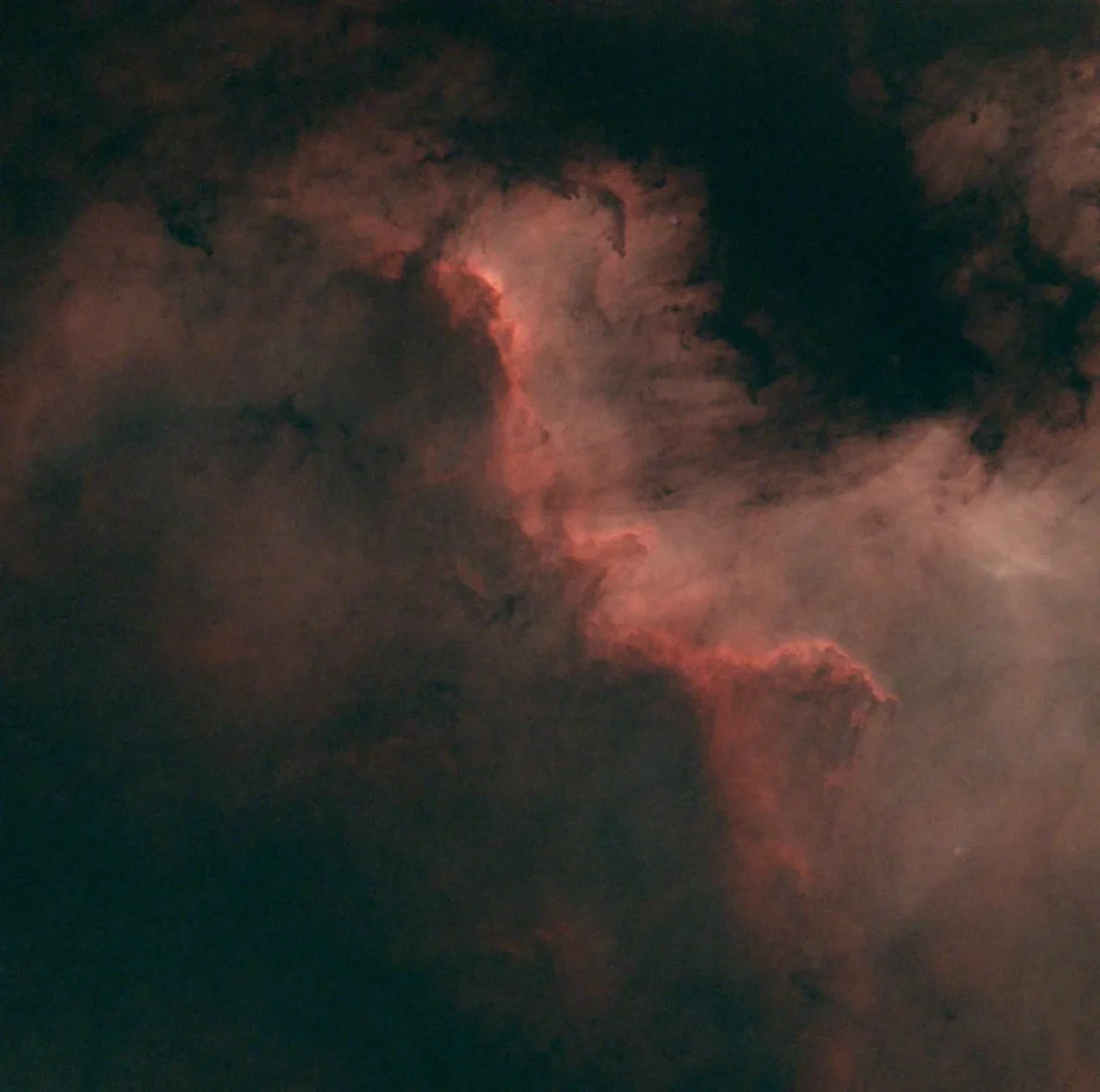


The Pelican Nebula (also known as IC 5070 and IC 5067) is an HII region associated with the North America Nebula in the constellation Cygnus. The image is the result of 30 minutes exposure (10×180 seconds, dark, flat, bias).
Note: Scroll the slider to switch between the images of the Pelican Nebula Nebula with the stars and its starless version.




